A 12 year old female comes to your office with her mother
because of a slightly raised painless rash which developed yesterday
morning. She notes swollen joints,
palpitations, and jerky uncontrolled movements.
You discover that she is visiting from Argentina and had a sore throat
and fever 3 weeks prior. She has a
temperature of 103.1 in the office today.
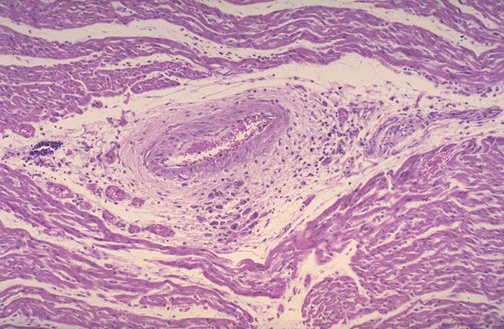
Below are tissue sections from heart biopsy.
What key features are present in the biopsy specimens?
1 1)Aschoff Body – lymphocytes, occasionally plasma
cells, and activated macrophages
2) Anitschkow cells (pathognomonic for RF) - activated histiocytes which have abundance cytoplasm and a central, slender, wavy, ribbon of chromatin. May become multinucleated. Characteristic “caterpillar chromatin.”
3) Fibrinoid necrosis, often perivascular
4) Verrucaw along the lines of valve closure overlying areas of fibrinoid necrosis within the cusps or along the chordae tendinae
2) Anitschkow cells (pathognomonic for RF) - activated histiocytes which have abundance cytoplasm and a central, slender, wavy, ribbon of chromatin. May become multinucleated. Characteristic “caterpillar chromatin.”
3) Fibrinoid necrosis, often perivascular
4) Verrucaw along the lines of valve closure overlying areas of fibrinoid necrosis within the cusps or along the chordae tendinae
What is the diagnosis?
Acute Rheumatic Fever
What is the pathogenesis?
Systemic illness following Group A
beta hemolytic strep pharyngitis. Due to
cross-reactivity of antibodies to strep antigens with host cardiac antigens
resulting in cardiac damage. ARF results
from immune response to group A strep.
What are the Jones criteria for RF? What do you need for
diagnosis?
Major Criteria:
1.
Migratory polyarthralgias
2.
Pancarditis
3.
Sydenham’s Chorea
4.
Erythema Marginatum
5.
Subcutaneous Nodules
Minor:
Fever,
Arthralgia, elevated ESR, CRP, PR, WBC
Dx: 2 major or 1 major + 2 minor + evidence of group a strep
infection
What organism would grow following cardiac culture?
None. Culture negative.
The patient returned after several more episodes of
rheumatic heart disease and died from complications from heart failur. Autopsy specimens are shown below:
What key findings are present in the autopsy specimens?
- Leaflet thickening
- 2 Thickening and fusion of the chordae tendinae
What valves are typically affected in rheumatic heart
disease?
Mitral>
Mitral + Aortic > Aortic Alone






No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.